MHI Receives 2020 Agency for Natural Resources and Energy Commissioner’s Award

Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Thermal Systems, Ltd. (MHI Thermal Systems), a part of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) Group, has won an Agency for Natural Resources and Energy Commissioner’s Award (Energy Savings Sector) in the “Product & Business Model” category at the 2020 Energy Conservation Grand Prize Awards sponsored by the Energy Conservation Center, Japan (ECCJ). This award was presented for the MSV2 series of air-cooled heat pump chillers(Note1) in recognition of its industry-leading coefficient of performance (COP)(Note2) achieved through a combination of the newly developed “e-3D scroll” compressor and other proprietary technologies. The awards ceremony will be held on January 27.
The MSV2 series comprises four models ranging from 40 to 70 horsepower (hp). These units incorporate the “e-3D scroll” compressor, a more advanced version of the “3D scroll” compressor that compresses the refrigerant from all directions. Modification to the scroll shape, from a step to a slope, has significantly reduced leakage loss, and provided a considerable gain in efficiency at low loads. In addition, the use of a large fan, long bell mouth, and small-diameter hairpin air heat exchanger provide 20% greater power efficiency compared to previous models. Further, this series offers approximately 55% energy reduction compared to absorption-type heating/cooling units.
The MSV2 series uses R32 refrigerant, which has around one-third the global warming potential (GWP)(Note3) of conventional R410A refrigerant. Along with a 28% reduction in refrigerant charge volume compared to previous models, and a 77% lower CO2 conversion factor, these units contribute to a lessening of the environmental load.
The ECCJ Energy Conservation Grand Prize Awards recognize outstanding energy-saving initiatives at businesses or workplaces that serve as examples for other companies, or outstanding energy-saving products and business models. The awards program was created to contribute to the realization of an energy-saving society by raising energy conservation awareness throughout Japan, and promoting the adoption of energy-saving products.
MHI Thermal Systems, encouraged by this award, will continue to develop technologies and products that provide further reductions in CO2 and energy savings. Further, by drawing on the collective technological capabilities realized through synergies generated from its broad business domain, including the thermal engineering business to enhance energy efficiency in a wide range of production plants, the large-scale refrigerator business for cooling large spaces, the air conditioning business to create a wide range of comfortable spaces, the transport refrigerating systems business essential to cold chains, and the automotive air-conditioning business, MHI Thermal Systems will focus on achieving optimal thermal solutions to meet the varied needs of customers.
- 1“Heat pump chiller” is a general term for a unit that creates and supplies hot and cold water for building air conditioning systems, or various types of industrial facilities. They are called “chillers” because they are used mainly in cooling applications, but the term “heat pump” is added because they can also be used to heat water to high temperatures. The internal system comprises refrigerant and water circulation systems, with heat exchanged as the refrigerant and water pass through a water heat exchanger.
- 2Coefficient of Performance (COP) is an indicator of the degree of efficiency that can be realized from using one kilowatt of electricity. Larger values indicate greater energy efficiency. For refrigeration systems, COP is the rated refrigeration capacity (kW) divided by electricity consumption (kW).
- 3Global Warming Potential (GWP) is a coefficient expressing a relative value, with CO2 fixed at a GWP of 1.0. Smaller values indicate greater environmental performance.
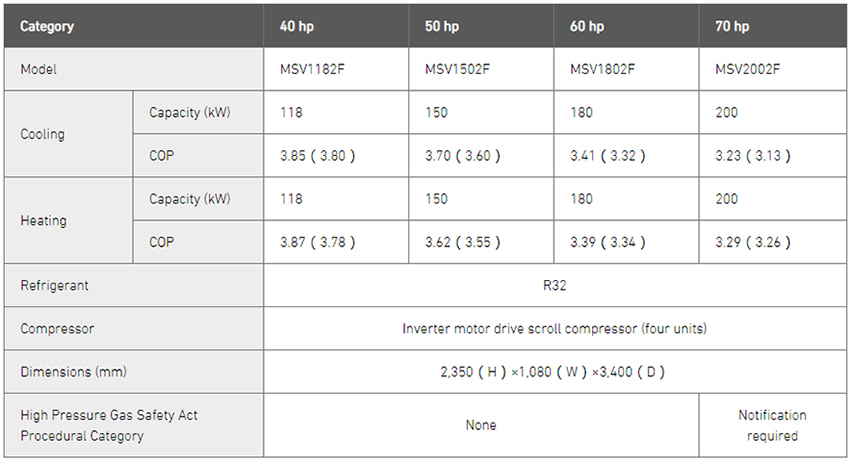
Allowable ranges of indicated values for cooling capacity, heating capacity, power consumption, and COP are based on JRA4066: 2017 “Water Chilling Unit”. Of note, values for power consumption and COP shown in the chart do not include internal pump power consumption in specifications with a built-in pump.
COP values are for 7℃ difference conditions. Figures in parentheses are 5℃ difference conditions.
Cooling condition: 7℃ difference = Cold water inlet temperature of 14℃ and outlet temperature of 7℃ at an external temperature of 35℃; 5℃ difference = Cold water inlet temperature of 12℃ and outlet temperature of 7℃ at an external temperature of 35℃.
Heating condition: 7℃ difference = Warm water inlet temperature of 38℃ and outlet temperature of 45℃ at an external temperature of 7℃DB (dry-bulb temperature) / 6℃WB (wet-bulb temperature); 5℃ difference = Warm water inlet temperature of 40℃ and outlet temperature of 45℃ at an external temperature of 7℃DB / 6℃WB.
To read the full article, please click here.
















